Download the guide
The Good Homes Alliance (GHA) and the British Blind and Shutter Association (BBSA) have launched a new design guide on shading for housing, seeking to embed a new culture – among building makers of all stripes – in which shading is central to a building’s design and built-in from the start.

The work has been led by an experienced team at award-winning architect Pollard Thomas Edwards (PTE), including sustainability lead Tom Dollard, author of ‘Designed to Perform’, Passivhaus designer Joseba Perez, and sustainable design specialist Raffaella Corrieri.
The guide was launched at a popular in-person event on 9th November at PTE’s offices at Diespeker Wharf in London, with talks from the wider project team which includes renowned engineering firm Max Fordham; Rajat Gupta, Professor of Sustainable Architecture and Climate Change at Oxford Brookes University, and construction consultants, Martin Arnold.

Why is the guide needed? Future proofing and climate resilience
As global temperatures continue to rise, so does the risk of buildings overheating. A recent study1 shows that by the middle of the 2030s, 90% of the UK housing stock will suffer from overheating. Simply put, our built environment – designed for dampness, breeze, rain and mild heat – is in no fit state to shelter us from this changing climate.
Currently in the UK, buildings are not required to pass the overheating criteria using future weather files to comply with the Building Regulations. Modelling using predicted future weather data has shown that buildings designed with shading products built-in from the start are less likely to overheat in the future than those that aren’t.
This guide calls for a new design culture in the UK. A design culture in which the everyday specification of shading products on domestic buildings – or the designing for shading from the start – is second nature among developers, housebuilders, architects and consultants.
The public too, buyers and tenants alike, should be well-versed in the benefits that shading products bring, in terms of reduced running costs, improved comfort and general wellbeing. The guide provides a shading ‘cheat sheet’ focused on the practicalities of adapting to holistic shading design.
What is in the guide?
A product section provides detailed information to help users to select the right product for a building’s shading needs. Each product page features a brief description, a table detailing its functionality, an in-situ product photograph, a ‘performance web’ visualising a product’s strengths and weaknesses and, where relevant, an architect’s comment on a product’s added value.
 The guide also provides a short history of shading design, explores UK-specific design challenges and wraps up with best practice advice.
The guide also provides a short history of shading design, explores UK-specific design challenges and wraps up with best practice advice.
The guidance is applicable to both new build and retrofit projects, and aimed at a range of stakeholders including architects, local authorities, planners, housing associations, developers, and policy makers.
Who has supported the guide?

Development of the guide has been supported by:
Ballymore – See case studies
Caribbean Blinds – See image gallery
Guthrie Douglas – See project gallery
Louvolite – See style blog
A steering group* of industry experts and stakeholders from across the sector has supported the development of the guide, with representatives from Architype, Greater Cambridge Shared Planning Service, CIBSE, ECD Architects, NDM Heath, OX Place, Sovereign, TOWN and Urban Light Surveyors.
Downloads

Download the guide
- File type: .pdf
- File size: 5mb
- Published: November 2023
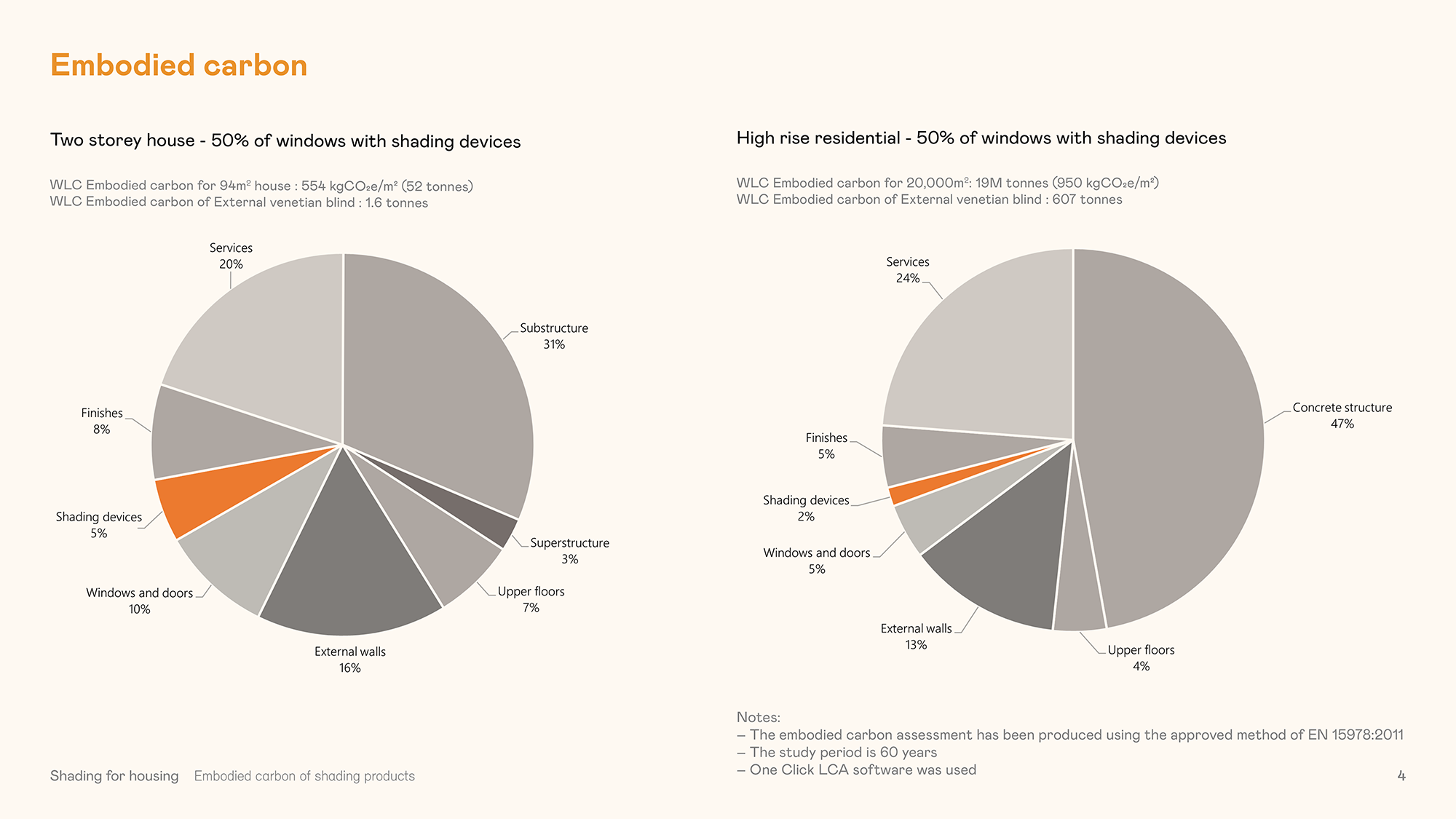
Additional report – ‘Embodied carbon of shading products‘
Quotes
“Since 2014, when Good Homes Alliance published ‘Preventing Overheating’ an evidence-based report on overheating and mitigation, we have worked on guidance and tools to mitigate overheating in homes. In 2019, we launched our tool and guidance to identify and mitigate overheating risks for new homes, followed by a version for retrofit and existing homes in 2022. This latest guidance expands on applicable strategies, seeking to influence decision making at an early stage, and provide the industry with the tools and knowledge to identify and integrate shading solutions as part of a holistic approach to resilience and aesthetics appropriate for our climate challenge.”
Lynne Sullivan OBE, Chair, Good Homes Alliance
“A guide like this, researched and prepared by a multi-disciplinary team from the built environment and the solar shading industry, is long overdue. The BBSA is proud to have been involved in developing such a practical and useful guide to help make our homes more energy efficient and comfortable, now and in the future.”
Andrew Chalk, Director of Operations, BBSA
“Our homes are overheating, and we simply can’t afford to address this with increasing mechanical ventilation or air conditioning. It is clear that shading must become a central component of design approaches to prevent increased overheating and unnecessary carbon emissions. I hope this guide goes some way to enable this necessary change in design culture, by increasing our knowledge and awareness of the range of shading types available, to help us design beautiful shading solutions that deliver improved outcomes for people and planet.”
Tom Dollard, Partner – Sustainability and Innovation, Pollard Thomas Edwards
“It is essential that the design of buildings prioritises future-proofing and protecting users from the effects of the climate emergency. As the earth’s climate warms and the thermal performance of buildings improves, overheating mitigation becomes more about keeping heat out of buildings, rather than in. Solar shading has a critical role to play in this. We hope this shading design guide will illustrate the opportunities for incorporating shading in buildings and help building owners, designers, and developers to choose the best option for their project.”
Kai Salman-Lord, Senior Building Performance Modeller, Max Fordham LLP
“Research studies have often raised the need for integrating shading in our homes for building long-term resilience against heat. For the first time, this report provides compressive evidence-based guidance on the performance of different shading products, to enable building design team and housing providers incorporate shading solutions for future-proofing new builds and retrofits.”
Professor Rajat Gupta, Professor of Sustainable Architecture and Climate Change, Oxford Brookes University
“The threat to life due to homes overheating in summer is rapidly overtaking the danger posed by lack of heating in winter. Solar shading can be the silver-bullet, regulating temperature whilst saving energy, and insulating properties in the winter too; but only if it is well-designed and not an afterthought. This guide is a great starting point for any specifier asking themselves how to achieve that.”
Andrew Kitching, Managing Director, Guthrie Douglas
“Climate change is no secret, and the issue of overheating will only become more apparent as time goes on. Whilst the solution to combat this problem already exists to an extent, solar shading products have an important part to play in helping our climate journey and need to be designed and incorporated from the outset.
Every measure needs to be taken to address the installation of solar shading during the design stage of any building in order to ensure its energy efficiency is at its highest, preventing the increasing number of homes from turning into unhabitable ‘greenhouses’ and ultimately cooling our planet.
This guide will go a long way in clearly setting out the ways in which the housebuilding industry can work together to minimise and mitigate overheating risk in new and existing homes. We’re proud to be helping raise awareness of this ever-growing and very real issue.”
Stuart Dantzic, Managing Director, Caribbean Blinds
* Full steering group list: Andrew Chalk, British Blind and Shutter Association; Dave Bush, British Blind and Shutter Association; Zoe de Grussa, British Blind and Shutter Association; Richard Broad, Good Homes Alliance; Julian Brooks, Good Homes Alliance; Rajat Gupta, Oxford Brookes University; Chris Martin, Martin Arnold; Anastasia Mylona, The Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers (CIBSE); Belen Alemany, Energy Conscious Design Architects (ECD); Debbie Haynes, OX Place; Emma Davies, Greater Cambridge Shared Planning Service; Nicholas Heath, NDM Heath; Gregory Francis, Urban Light Surveyors; Adrian Coe, Urban Light Surveyors; Richard Young, Sovereign; Steve Birtles, Louvolite; Stuart Dantzic, Caribbean Blinds; Andy Kitching, Guthrie Douglas; Aaron Caffrey, Ballymore; Bryn Marler, Ballymore; Neil Murphy, TOWN; Seb Laan Lomas, Architype.
1 ARUP, Addressing overheating risk in existing UK homes (2022) An Arup report commissioned by the Climate Change Committee; retrieved online September 2023.
Further information
Good Homes Alliance – A sustainability organisation with a focus on net zero, new build homes and building performance. Membership network of 120+ members from across industry including architects and consultants, plus 30+ local authorities, housing associations and private sector developers, who are set to build 120,000 new homes over the next 10 years.
The shading guide follows on from popular industry guidance developed by GHA on minimising and mitigating overheating risk in new and existing homes.
British Blind and Shutter Association (BBSA) – A national trade association with 500+ members that manufacture, supply and install interior and exterior blinds, awnings, security grilles and shutters and associated motor and control systems.
For more information about the project, please contact Richard Broad, Projects Manager, Good Homes Alliance – richard@goodhomes.org.uk.
The contents of this guide and appendices are for information purposes and provide general guidance only. The subject matter covered in this guidance is not exhaustive. Relevant standards and approved documents should be fully consulted.
© Good Homes Alliance (GHA) and British Blind and Shutter Association (BBSA), 2023. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without the express written permission of the GHA and BBSA.








 The guide also provides a short history of shading design, explores UK-specific design challenges and wraps up with best practice advice.
The guide also provides a short history of shading design, explores UK-specific design challenges and wraps up with best practice advice.



















